3D Object Detection
Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey
Regularly updated project page : https://github.com/The-Learning-And-Vision-Atelier-LAVA/SoTA-Point-Cloud
1. INTRODUCTION
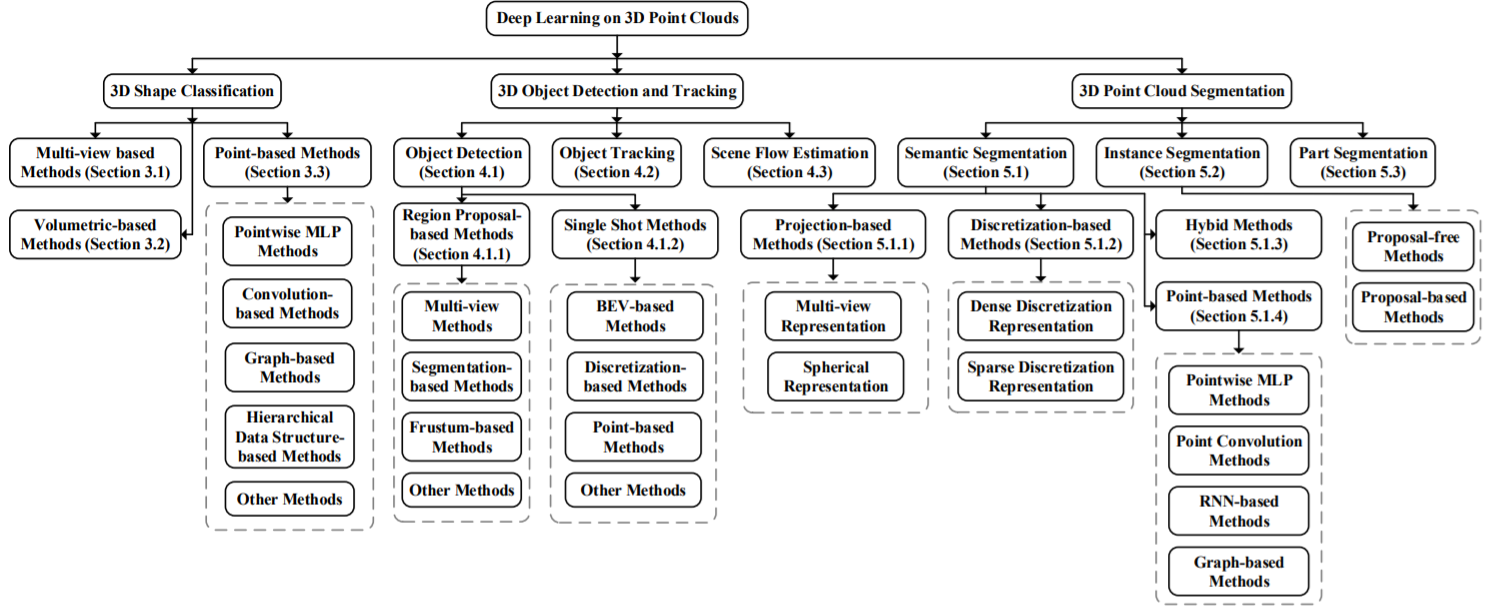
2. BACKGROUND
2.1 Datasets
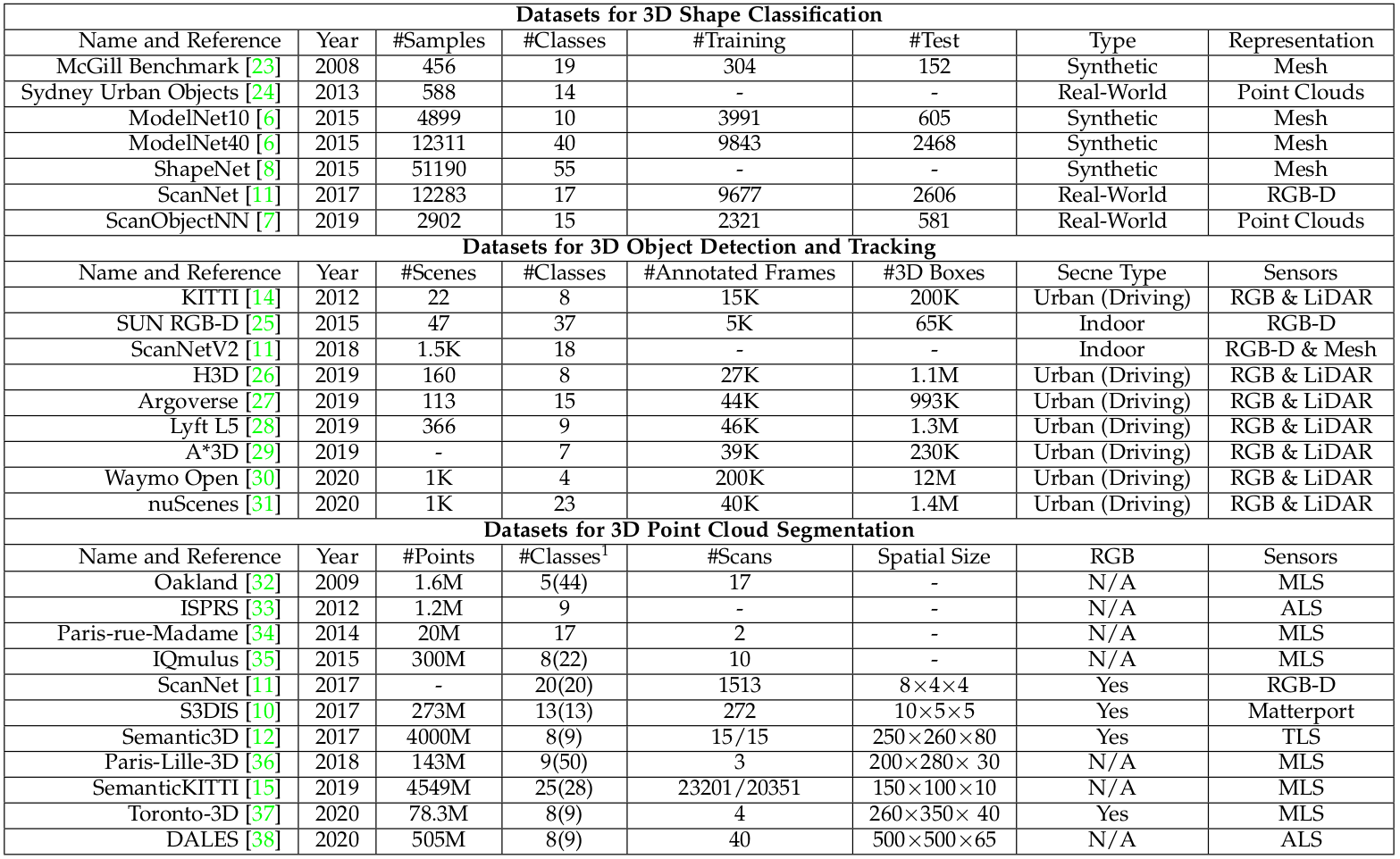
2.1.1 Dataset for 3D shape classification
- 3D Shape Classification Dataset에는 크게 2가지 Type이 있다. Synthetic datasets & Real-world datasets
- Synthetic dataset에 있는 Object는 겹침이나 배경같은 Data가 없이 깔끔하다
-
반면에, real-world dataset에 있는 Object들은 다른 층의 Object에 가려지고 일부 Object가 배경으로 오염되어 있기도 하다.
- McGill Benchmark
- Sydney Urban Objects
- ModelNet10
- ModelNet40
- ShapeNet
- ScanNet
- ScanObjectNN
2.1.2 Dataset for 3D object detection and tracking
- 3D object detection and tracking Dataset에는 2가지 종류가 있다. indoor scenes and outdoor urban scenes.
- indoor dataset의 point clouds는 dense depth maps나 sampled from 3D meshes를 변환해서 만듭니다.
-
outdoor urban datasets은 자율주행용으로 만들어졌으며 객체는 공간적으로 잘 분리되어 있으며 이러한 포인트 클라우드는 희소(sparse)합니다.
- KITTI
- SUN RGB-D
- ScanNetV2
- H3D
- Argoverse
- Lyft L5
- A*3D
- Waymo Open
- nuScenes
2.1.3 Dataset for 3D point cloud segmentation
- 3D point cloud segmentation용 datasets은 다음과 같은 다양한 Sensor로 얻어집니다.
-
이러한 Dataset들은 오답탐지 , Shape 불완전성 , class imbalance와 같은 어려운 과제를 해결하는데 도움을 줄 수 있다.
- Oakland
- ISPRS
- Paris-rue-Madame
- IQmulus
- ScanNet
- S3DIS
- Semantic3D
- Paris-Lille-3D
- SemanticKITTI
- Toronto-3D
- DALES
2.2 Evaluation Metrics
2.2.1 3D shape classification
- Overall Accuracy (OA) : the mean accuracy for all test instances
- mean class accuracy (mAcc) : the mean accuracy for all shape classes
2.2.2 3D object detection
- Average Precision (AP) : the most frequently used criterion. calculated as the area under the precision-recall curve.
2.2.3 3D single object tracker
- Precision and Success : commonly used to evaluate the overall performance
2.2.4 3D multi-object tracking
- Average Multi-Object Tracking Accuracy (AMOTA)
- Average Multi-Object Tracking Precision (AMOTP)
2.2.5 3D point cloud segmentation
- Overall Accuracy (OA)
- mean Intersection over Union (mIoU)
- mean class Accuracy (mAcc)
- mean Average Precision (mAP) : also used in instance segmentation of 3D point clouds.
3. 3D SHAPE CLASSIFICATION
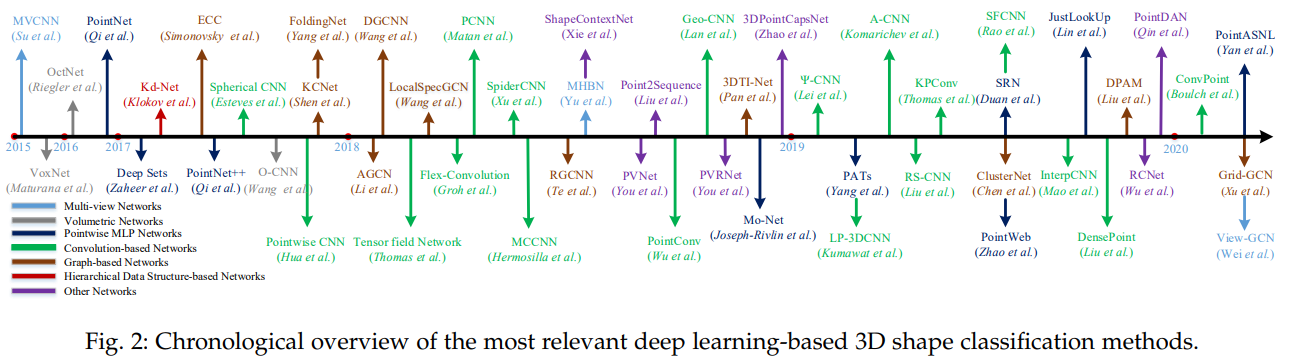
- 신경망 입력 Data Type에 따른 분류(According to the data type of input for neural networks)
- multi-view based
- project an unstructured point cloud into 2D images
- volumetric-based
- convert a point cloud into a 3D volumetric representation
⇒ well-established 2D or 3D convolutional networks are leveraged to achieve shape classification
- convert a point cloud into a 3D volumetric representation
- point-based methods
- directly work on raw point clouds without any voxelization or projection
- do not introduce explicit information loss and become increasingly popular.
- multi-view based
3.1 Multi-view based Methods**
- 이 방법은 먼저 3D Shape을 multiple views로 Project시킨 후에 다양한 Feature를 조합하여 정확한 Shape classification을 수행한다.
-
다양한 Feature들을 어떻게 조합하여 Shape을 Classification하는지가 이 방법의 중요한 Key이다.
- MVCNN
- MHBN
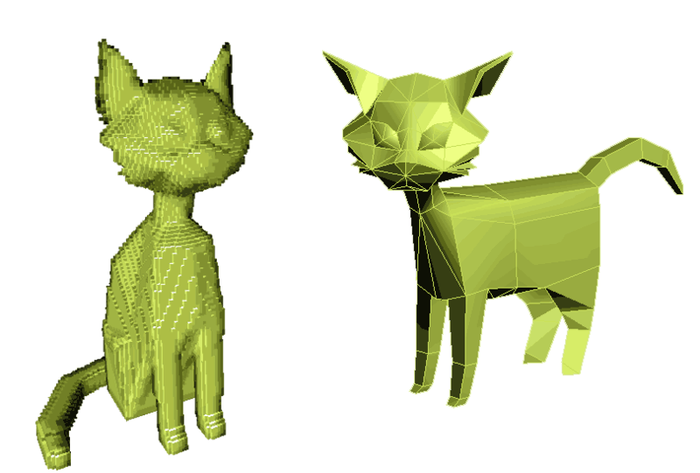
3.2 Volumetric-based Methods
-
이 방법은 shape classification하기 위해서 point cloud를 3D grids로 voxelization 시킨 후에 3D Convolution Neural Network (CNN)을 적용한다.
-
Voxelization
⇒ Pixel의 3D 형태가 Voxel이므로, Voxel은 그래픽을 구성하는 정육면체 모양의 요소라고 생각하면 된다. Pixel과 마찬가지로 모든 Voxel의 모양과 크기는 동일하고. 색상값을 가지며 3D 이미지를 구성하게 된다.
* VoxNet
* ShapeNets
* OctNet
* Octree-based CNN
* PointGrid
3.3 Point-based Methods
- 각 Point의 Feature 학습에 사용된 Network architecture에 따라서 다음과 같은 방식이 있다.
- pointwise MLP
- convolution-based
- graph-based
- hierarchical data structure-based
- Others
3.3.1 Pointwise MLP Methods
- 이러한 방법은 여러 공유 MLP(Multi-Layer Perceptron)를 사용하여 각 점을 독립적으로 모델링한 다음 아래 그림과 같이 symmetric aggregation function을 사용하여 global feature을 모은다.
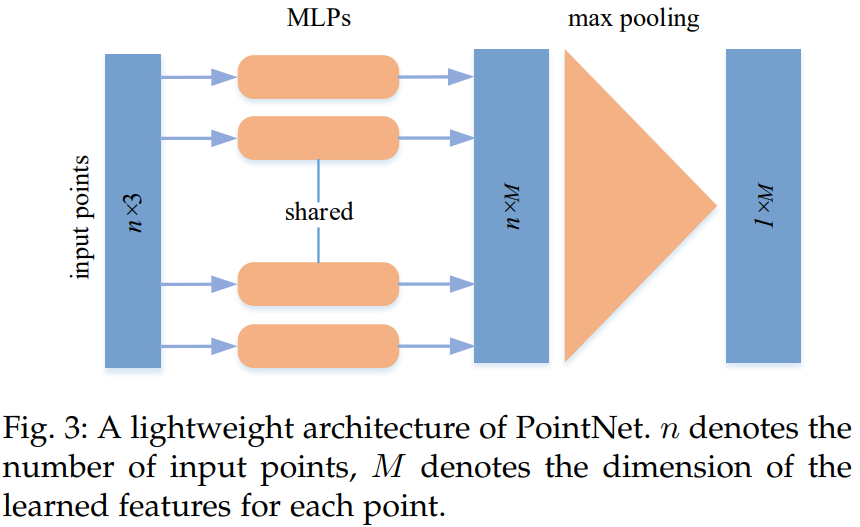
* PointNet
* Deep sets
* PointNet++
* Mo-Net
* Point Attention Transformers (PATs)
* PointWeb
* Structural Relational Network (SRN)
* SRINet
* PointASNL
3.3.2 Convolution-based Methods
- Image에 적용하는 2D Kernel과 비교해서 Point Cloud에 적용하는 3D CNN Kernel은 Point Cloud의 irregularity 한 특성 때문에 Design하기 어렵다.
- convolutional kernel의 종류에 따라, 3D convolution 방법은 아래 그림과 같이 continuous convolution methods와 discrete convolution methods로 나뉜다.
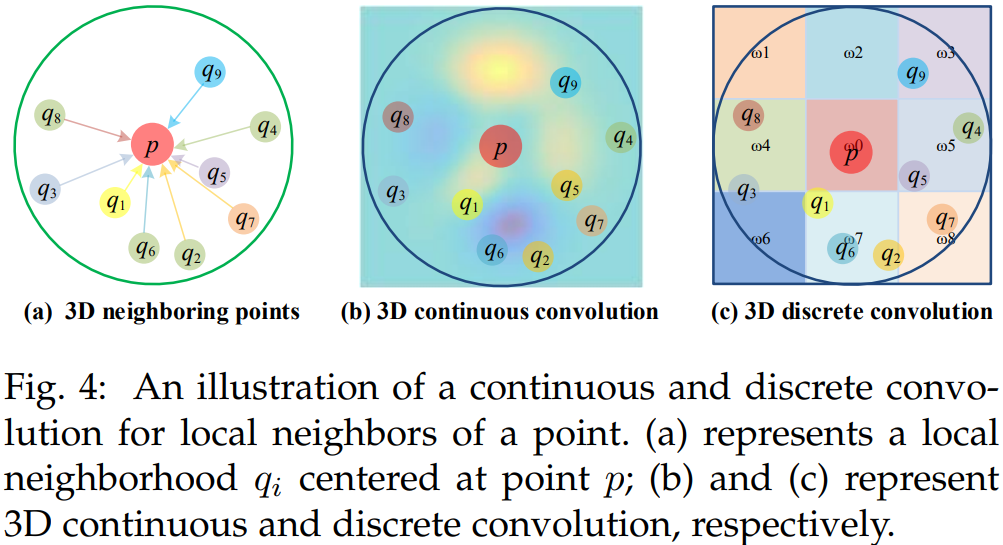
3.3.2.1 3D Continuous Convolution Methods
- 이 방법은 continuous space에서 convolutional kernels을 정의합니다. 여기서 neighboring points의 Weight는 center point에 대한 공간 분포와 관련됩니다.
- RS-CNN
- DensePoint
- Kernel Point Convolution (KPConv)
- ConvPoint
- PointConv
- MCCNN
- SpiderCNN
- PCNN
- 3D Spherical CNN
- Tensor field networks
- SPHNet
- Flex-Convolution
3.3.2.2 3D Discrete Convolution Methods
- 이 방법은 neighboring points의 Weight가 center point에 대한 오프셋과 관련된 일반 그리드에서 convolutional kernels을 정의합니다.
- GeoConv
- PointCNN
- InterpConv
- RIConv
- A-CNN
- SFCNN
3.3.3 Graph-based Methods
- Graph Based Network은 Point Cloud의 각 점을 Graph의 Vertex로 생각하고 방향이 있는 Graph를 생성한다.
- Feature Learning은 그 이후에 spatial or spectral domains에서 실행한다.
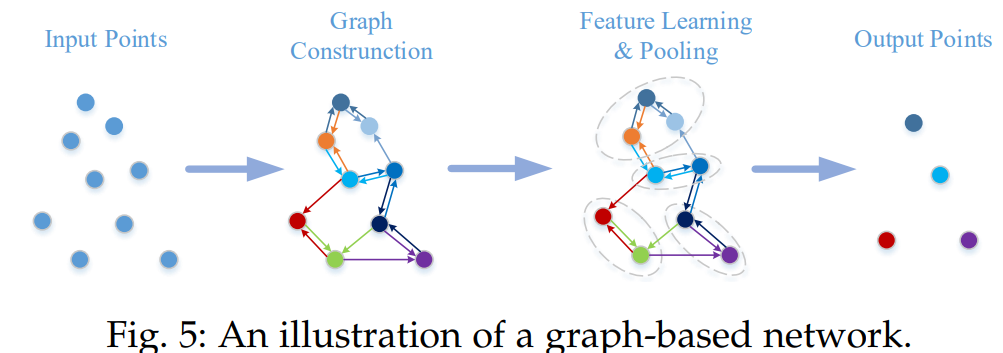
3.3.3.1 Graph-based Methods in Spatial Domain
- 공간 Domain에서 convolution & pooling 정의
- 인접 점들에 MLP를 적용하여 새로운 coarsened graph를 만들고 여기서 Feature를 뽑는다.
- 각 Vertex의 Feature는 보통 좌표 / Laser 강도 / 색상등으로 정의되고, Edge의 Feature는 각 점들의 연결의 기하학적 특징으로 할당된다.
* EdgeConditioned Convolution (ECC)
* VoxelGrid
* DGCNN
* EdgeConv
* LDGCNN
* FoldingNet
* Dynamic Points Agglomeration Module (DPAM)
* KCNet
* G3D
* ClusterNet
* Grid-GCN
3.3.3.2 Graph-based Methods in Spectral Domain
-
Conv.를 Graph의 신호를 Laplacian matrix 고유 벡터와 곱하는 것으로 정의하는 spectral filtering로 정의하여 구현
- RGCNN
- AGCN
- HGNN
- LocalSpecGCN
- PointGCN
- 3DTI-Net
3.3.4 Hierarchical Data Structure-based Methods
- 이 방법은 다양한 hierarchical data structures (e.g., octree and kd-tree)를 기초로 해서 구성된다.
- 이 방법은 각 점들의 Feature를 Tree의 Leaf Node에서 Root Node로 따라 올라가면서 학습하게 된다.
- OctNet
- Kd-Net
- 3DContextNet
- SO-Net
- SOM
3.3.5 Other Methods
- RBFNet
- 3DPointCapsNet
- PointDAN
- ShapeContextNet
- RCNet
- RCNet-E
- Point2Sequences
- PVNet
- PVRNet
3.5 Summary
- Pointwise MLP networks는 다른 종류의 Network의 Basic Building Block으로 자주 사용된다.
- standard deep learning architecture로써, convolution-based networks는 불규칙한 3D Point Clould에서 우수한 성능을 보여준다.
- 불규칙한 Data에서 discrete and continuous convolution networks 에 좀 더 많은 관심을 기울일 필요가 있다.
- 불규칙한 data를 다루는 내재된 훌륭한 성능 덕분에 graph-based networks은 최근 많은 관심을 받고 있다.
- 하지만 spectral domain에서 다양한 Graph 구조로 확장시키는 것은 여전히 어려운 일이다.

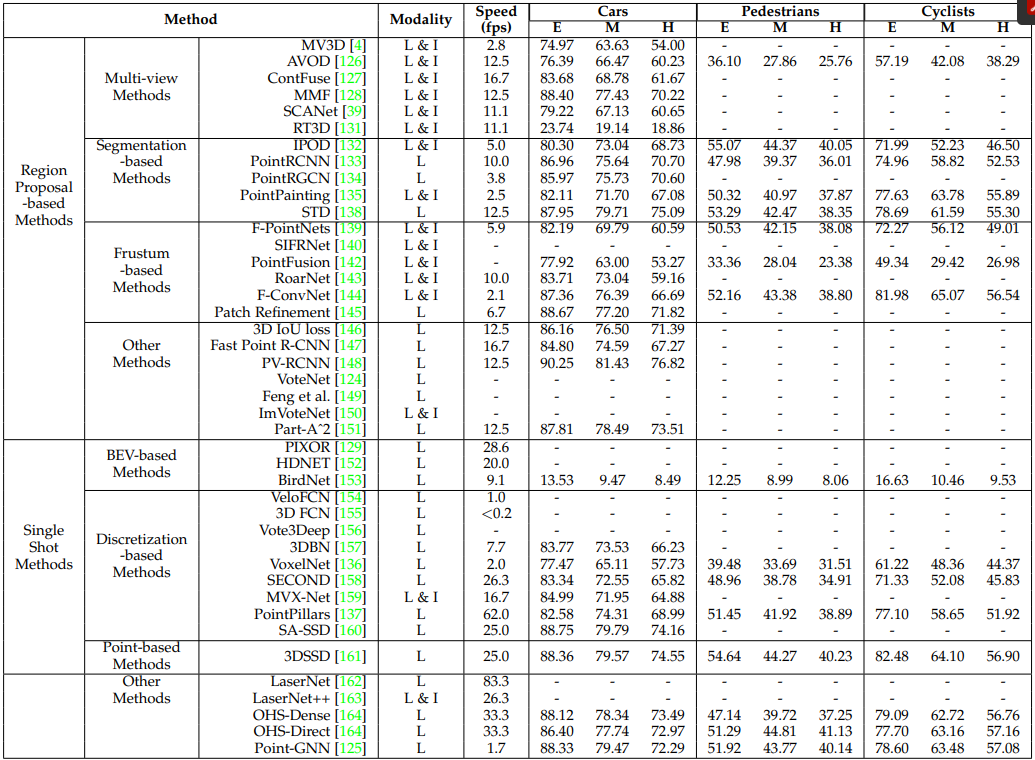
4. 3D OBJECT DETECTION AND TRACKING
4.1 3D Object Detection
- 일반적인 3D object detector는 Point Cloud의 장면을 입력으로 받아서 각 Object의 oriented 3D bounding를 만들어 냅니다.
- 2D Image의 object detection과 유사하게, 3D object detection 방법은 크게 region proposal based and single shot methods의 2가지로 나눌 수 있다.
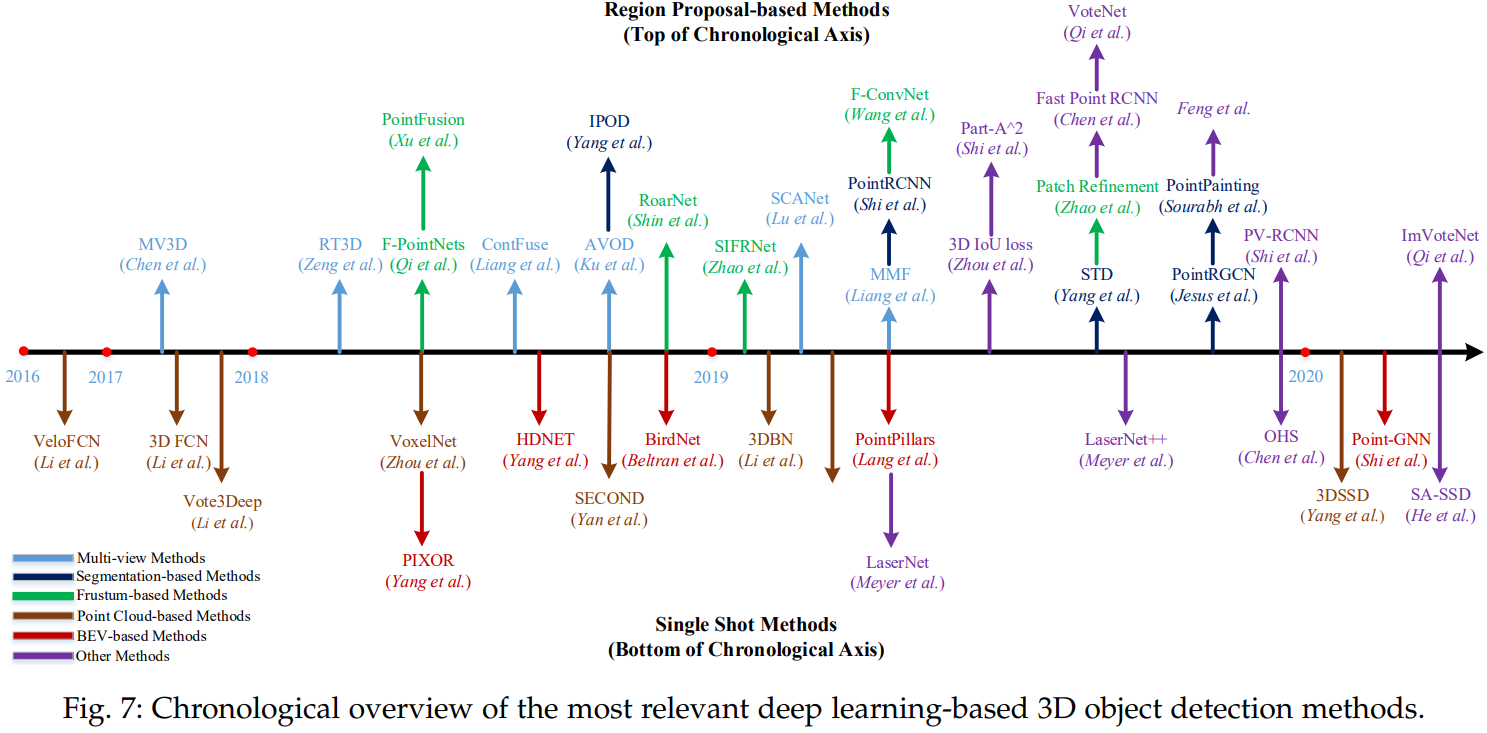
4.1.1 Region Proposal-based Methods
- 이 방법은 우선 몇개의 Object를 포함하는 Region(Proposals이라고도 불린다)을 제안하고 각 Proposal에서 Feature를 추출하여 분류합니다.
- 각 방법이 제안하는 Proposal 생성 방법에 따르면, 이 방법도 크게 3가지로 나눌 수 있습니다.
4.1.1.1 Multi-view based Methods
- 이 방법은 다양한 소스의 Data로 부터 Feature를 얻는다.
- Computational Cost가 높다
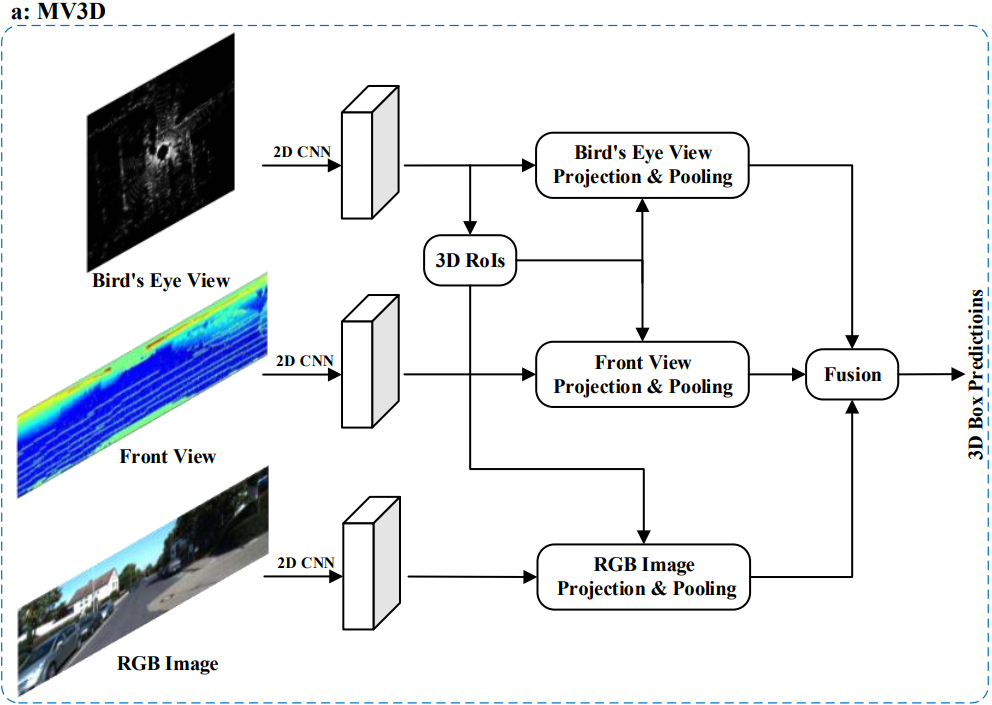
- 실사용에서 사용하기에는 너무 느리기 때문에 성능 향상을 위한 방안 발전
- Multi Modality로부터 얻은 Data를 효율적으로 연결하기 위한 방법
- Robust한 Data를 뽑기 위한 방안
- MV3D
- AVOD
- ContFuse
- MMF
- SCANet
- RT3D
4.1.1.2 Segmentation-based Methods
- 이 방법은 먼저 기존의 semantic segmentation techniques을 이용하여 대부분의 background points를 제거한 후, 나머지 Point들로부터 large amount of high-quality proposals을 생성하는 방법이다.
- multi-view methods와 비교하면, 이 방법은 higher object recall rates를 달성할 수 있고, 복잡한 장면에 좀 더 적합하다.
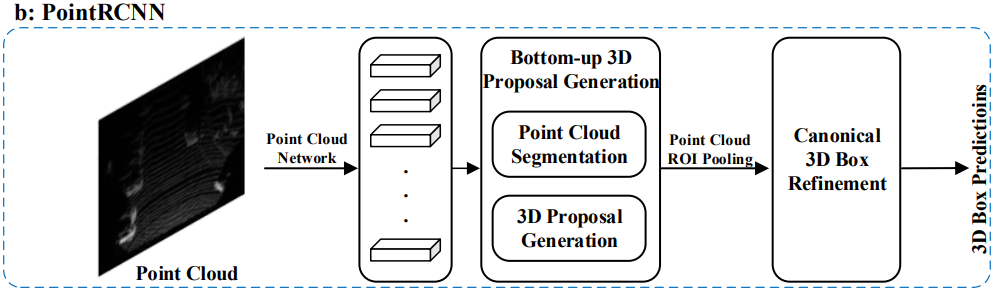
- IPOD
- PointRCNN
- PointRGCN
- PointPainting
- STD
4.1.1.3 Frustum-based Methods
- 이 방법은 기존의 2D object detectors를 이용하여 2D regions candidate 을 먼저 찾아내고, 그 후에 각각의 2D regions candidate에서 3D frustum proposal 을 찾아내는 방법이다.
- 이 방법이 3D objects의 위치를 효과적으로 찾는다 해도, 2D image detectors의 성능 한계에 영향을 받습니다.
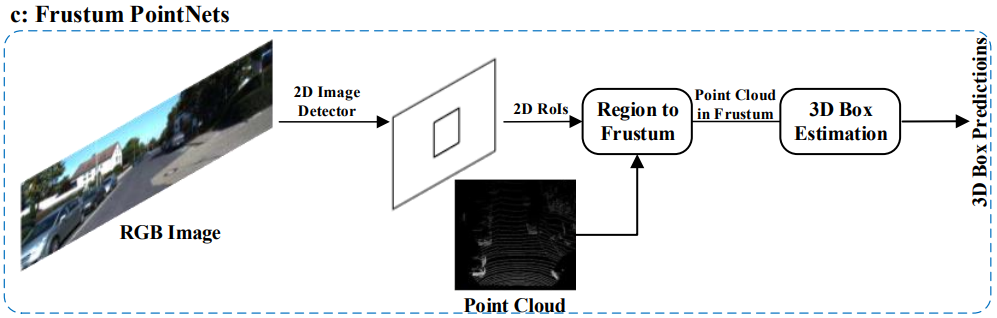
* F-PointNets
* SIFRNet
* PointFusion
* RoarNet
* F-ConvNet
* Patch Refinement
4.1.1.4 Other Methods
- 3D IoU loss
- Fast Point R-CNN
- PV-RCNN
- VoteNet
- Feng et al.
- ImVoteNet
- Part-A^2
4.1.2 Single Shot Methods
- 이 방법은 single-stage network을 이용해서 바로 class probabilities를 예측하고 3D bounding boxes를 찾아냅니다.
- 이 방법은 region proposal generation을 할 필요도 없고 post-processing도 필요하지 않아서, 결과적으로 빠른 속도를 보여줍니다.
- Input Data의 Type에 따라서 BEV-based, discretizationbased , point-based methods로 나눌 수 있습니다.
4.1.2.1 BEV-based Methods ( BEV : Bird’s Eye View )
이 방법은 입력으로 BEV Data Representation을 받는다.
- PIXOR
- HDNET
- BirdNet
4.1.2.2 Discretization-based Methods
- 이 방법은 Point Cloud를 일반적인 discrete representation으로 바꾼 후에 CNN을 적용하여 분류하는 방법이다.
- VeloFCN
- 3D FCN
- Vote3Deep
- 3DBN
- VoxelNet
- SECOND
- MVX-Net
- PointPillars
- SA-SSD
4.1.2.3 Point-based Methods
- 이 방법은 Raw Point Cloud 값을 Direct로 받습니다.
- 3DSSD
4.1.2.4 Other Methods
- LaserNet
- LaserNet++
- OHS-Dense
- OHS-Direct
- Point-GNN
4.2 3D Object Tracking
- 어떤 객체의 첫번째 Frame에서의 위치가 주어졌을 때 object tracking은 다음 Frame들에서 위치를 추정하는 것이다.
-
3D object tracking은 Point Cloud의 기하학적 정보를 사용할 수 있기 때문에 이미지 기반 추적이 직면한 여러 단점을 극복할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 3D Siamese network
- STAPLECA
- SiamFC
- Point-to-Box (P2B)
4.3 3D Scene Flow Estimation
- Point Cloud에서 3D Scene Flow Estimation은 주어진 Point Cloud X,Y에서 X에 속한 xi에서 그에 해당하는 Y의 xi’로의 이동을 나타낸다.
* FlowNet3D
* Hierarchical Permutohedral Lattice FlowNet (HPLFlowNet)
* PointRNN , PointGRU , PointLSTM
4.4 Summary
- Region proposal-based 방법과 single shot 방법 중에 Region proposal-based 방법은 가장 많이 연구되고 있고, single shot 방법은 KITTI test 3D 과 BEV benchmarks에서 더 나은 성능을 보여준다.
- 현재의 3D object detectors에는 크게 2가지의 한계점이 있다. 먼저, long-range detection 능력이 상대적으로 좋지 않다. 둘째, Image로부터 얻은 정보를 어떻게 하면 최대한으로 활용할지는 아직 연구할 것이 많이 남아 있다.
- Multi-task learning은 3D object detection 분야가 나아가야할 미래이다. 예를 들어, MMF는 incorporating multiple tasks를 통해서 SOTA를 달성하기 위해서 cross-modality representation을 학습한다.
- 3D object tracking and scene flow estimation은 research topics으로 떠오르고 있으며, 2019년 이후로 점차 주목을 받고 있다.
5. 3D POINT CLOUD SEGMENTATION
- 3D point cloud segmentation는 global geometric structure와 각 Point의 fine-grained details에 대한 이해가 필요하다.
-
3D point cloud segmentation 방법은 segmentation 단위에 따라서 3가지로 나눌 수 있다.
- semantic segmentation (scene level)
- instance segmentation (object level)
- part segmentation (part level)
5.1 3D semantic segmentation
- semantic segmentation : 인공지능이 이미지에 있는 객체를 픽셀 단위로 분류하는 것
- Point Cloud가 있을 때, semantic segmentation의 목적은 Point의 semantic meaning에 따라서 여러개의 하위 집합으로 분리하는 것이다.
-
3D shape classification의 종류를 분류한 것과 비슷하게, semantic segmentation에는 크게 4가지의 paradigms이 있다.
- projection-based
- discretizationbased
- point-based
- hybrid methods.
- projection과 discretizationbased 방법의 첫번째 순서는 multi-view, spherical, volumetric, permutohedral lattice , hybrid representations 등과 같은 intermediate regular representation 형태의 Point Cloud 표현 방식으로 변환하는 것이다.
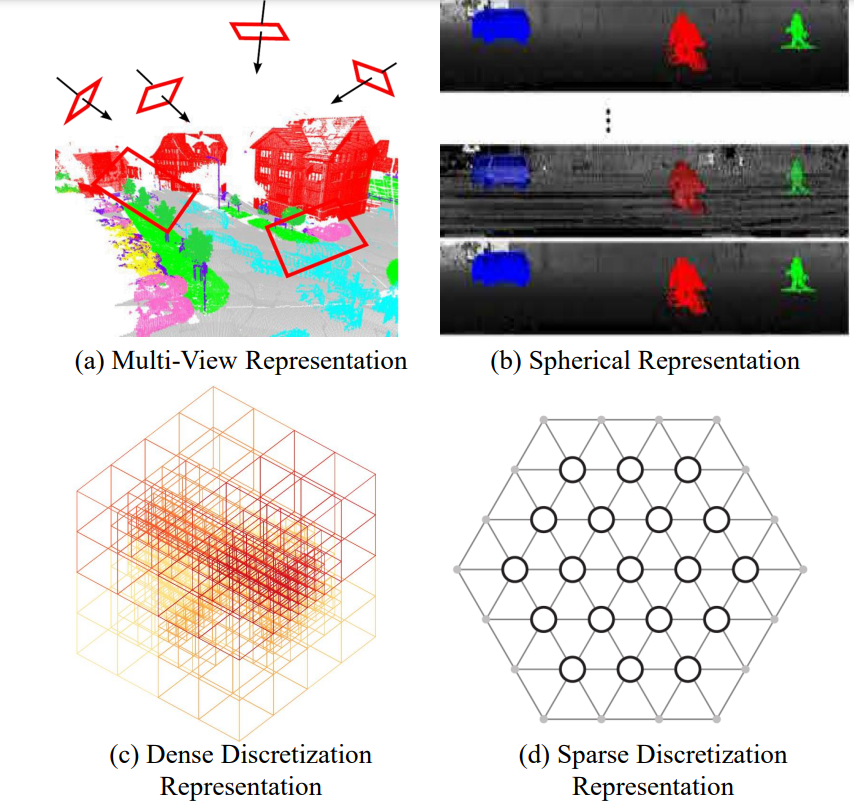
- 그런 다음에 intermediate segmentation 결과는 Raw point cloud에 다시 투영(Project)됩니다.
- 반면에, point-based 방법은 irregular point clouds로 바로 동작합니다.
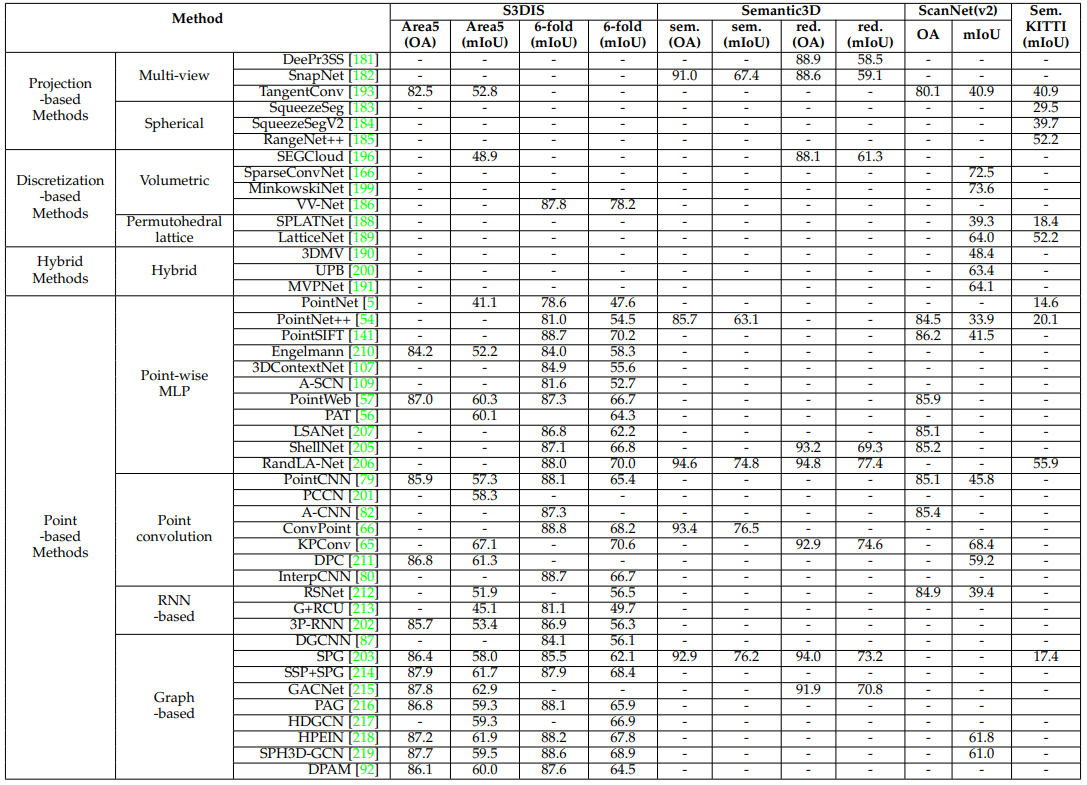
5.1.1 Projection-based Methods
- 이 방법은 보통 3D point cloud를 2D Image로 Project시킨다
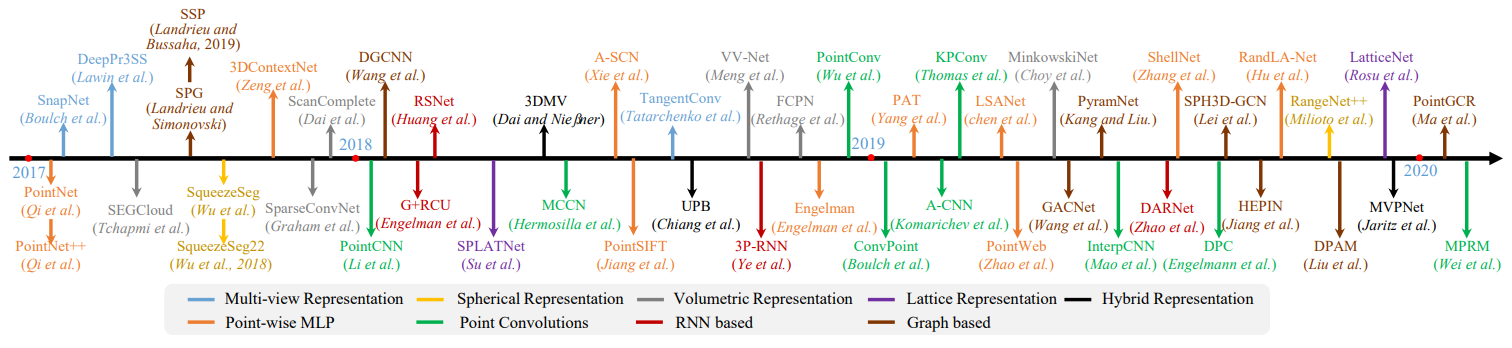
5.1.1.1 Multi-view Representation
- DeePr3SS
- SnapNet
- TangentConv
5.1.1.2 Spherical Representation
- SqueezeSeg
- SqueezeSegV2
- RangeNet++
5.1.2 Discretization-based Methods
- 이 방법은 보통 point cloud를 volumetric 이나 sparse permutohedral lattices 같은 dense/sparse discrete 표현으로 변환합니다.
5.1.2.1 Volumetric( Dense Discretization Representation )
- SEGCloud
- SparseConvNet
- MinkowskiNet
- VV-Net
5.1.2.2 Permutohedral lattice( Sparse Discretization Representation )
- SPLATNet
- LatticeNet
5.1.3 Hybrid Methods
- 3DMV
- UPB
- MVPNet
5.1.4 Point-based Methods
- Point-based networks는 irregular한 point clouds를 바로 Data로 사용한다.
- 하지만, point clouds는 orderless 하고 unstructured하기 때문에 standard CNN에 바로 적용하지 못한다.
- 이를 극복하기 위해서 선구자적인 연구인 PointNet이 제안되었다. PointNet은 Shared MLP를 사용하여 Point별 Feature를 학습하고 symmetrical pooling function을 이용하여 global feature를 학습한다.
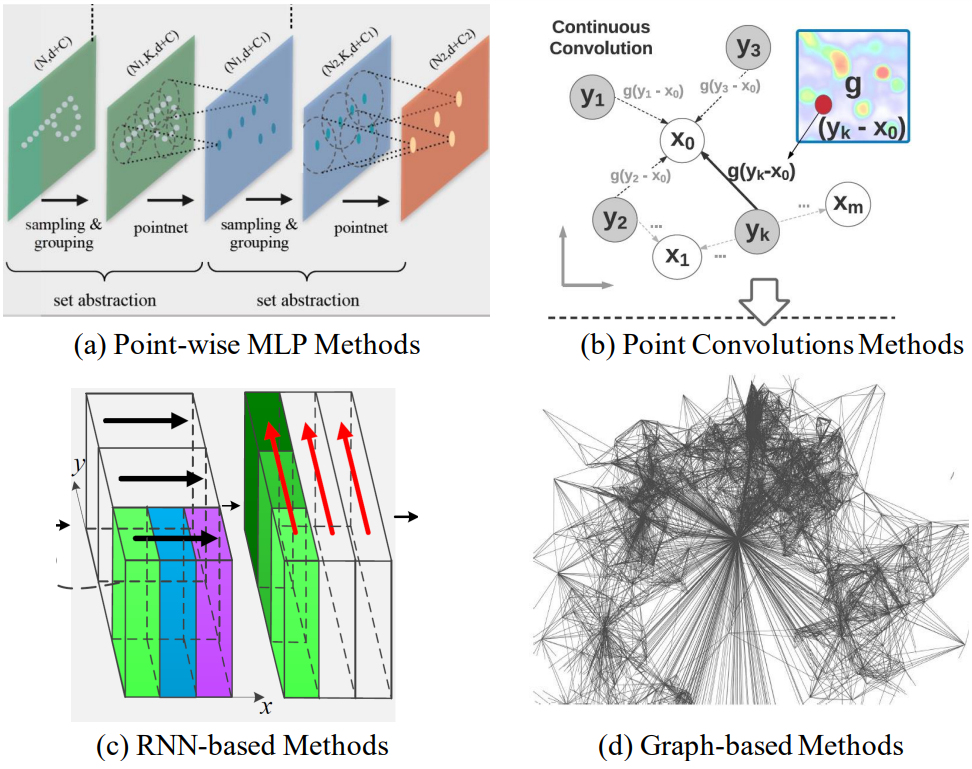
5.1.4.1 Pointwise MLP Methods
- 이 방법은 기본적으로 high efficiency를 위해서 shared MLP를 basic unit으로 사용한다.
- 하지만, shared MLP에 의한 Extracted된 point-wise features는 point clouds의 local geometry를 잡아내지 못하고 또한 Point들 간의 상호 작용도 잡지 못한다.
-
이런 단점을 극복하고 richer local structures와 각 Point들의 wider context를 잡아내기 위해서 neighboring feature pooling, attentionbased aggregation, local-global feature concatenation등을 기본으로 하는 몇몇 Network들이 소개되었다.
- PointNet
- PointNet++
- PointSIFT
- Engelmann
- 3DContextNet
- A-SCN
- PointWeb
- PAT
- LSANet
- ShellNet
- RandLA-Net
5.1.4.2 Point Convolution Methods
-
이 방법은 Point Cloud에 효과적인 convolution operators를 제안하고자 한다.
- PointCNN
- PCCN
- A-CNN
- ConvPoint
- KPConv
- DPC
- InterpCNN
5.1.4.3 RNN-based Methods
-
Point Cloud에 내재된 context features를 잡아내기 위해 RNN도 사용된다.
- RSNet
- G+RCU
- 3P-RNN
5.1.4.4 Graph-based Methods
-
3D point clouds의 드러나지 않는 모양과 geometric structure를 잡아내기 위해서 Graph Network을 이용한 몇몇 방법들이 있다.
- DGCNN
- SPG
- SSP+SPG
- GACNet
- PAG
- HDGCN
- HPEIN
- SPH3D-GCN
- DPAM
5.2 Instance Segmentation
- semantic segmentation에 비교해서 instance segmentation는 Point에 대한 보다 정확하고 세분화된 추론이 필요하기 때문에 더 어렵습니다.
- 특히, instance segmentation은 각 Point들의 의미론적 구분도 해야할 뿐만 아니라 같은 의미를 가진 Point들을 분리도 해야 합니다.
- instance segmentation은 크게 proposal-based methods and proposal-free methods로 나눌 수 있다.
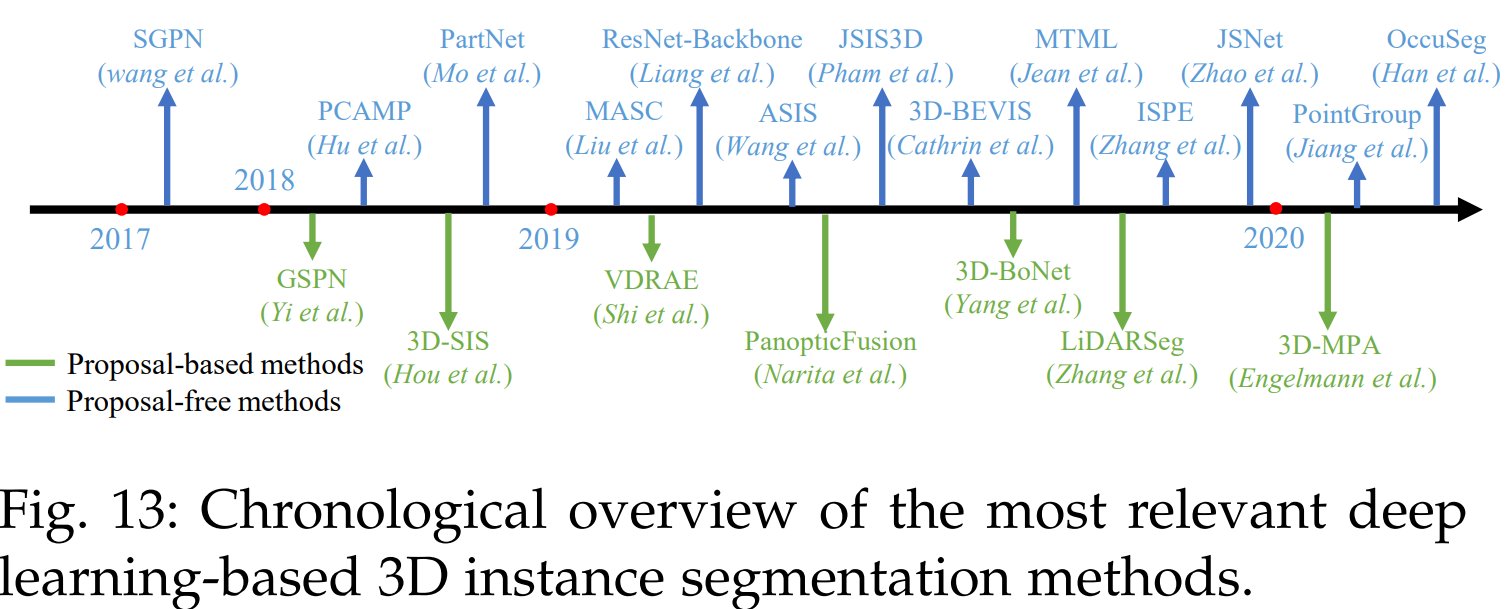
5.2.1 Proposal-based Methods
- 이 방법은 instance segmentation 문제를 3D object detection 과 instance mask prediction 2개의 하위 문제로 변환합니다.
- 전체적으로, proposal-based methods은 간단하고 직관적이며, 결과는 대체적으로 좋은 물체성 / 대상성(objectness)을 가진다.
- 하지만, 이 방법은 multi-stage training이 요구되고 중복된 제안 결과를 걸러내야 한다는 단점이 있습니다.
-
그래서, 대체로 이 방법은 시간이 오래걸리고 많은 계산량이 요구됩니다.
- GSPN
- 3D-SIS
- VDRAE
- PanopticFusion
- 3D-BoNe
- LiDARSeg
- 3D-MPA
5.2.2 Proposal-free Methods
- Proposal-free methods 방식은 object detection module이 없다.
- 대신, 이 방식은 semantic segmentation 후에 subsequent clustering 을 하는 방식으로 진행합니다.
- 특히, 대부분의 Proposal-free methods는 같은 Instance에 속하는 Point들은 모두 매우 유사한 Feature들을 가지고 있을 것이라는 가정을 합니다.
- 그러므로, 이 방법은 주로 discriminative feature learning 및 point grouping에 중점을 둡니다.
- proposal-free methods는 region-proposal와 같은 계산량이 매우 높은 방식이 필요하지 않습니다.
-
하지만, 이 방법으로 구분된 instance segments의 대상성(objectness)는 보통 명시적인 Object boundaries가 없기 때문에 좋지 않다.
- SGPN
- PCAMP
- PartNet
- ResNet-Backbone
- JSIS3D
- MTML
- ISPE
- JSNet
- PointGroup
- OccuSeg
5.3 Part Segmentation
- part segmentation 의 어려움은 다음 2가지이다.
- 첫째로, 동일한 semantic 레이블을 가진 Part는 기하학적 다양성과 모호성이 크다
-
둘째로, 동일한 semantic의 객체를 구성하는 part의 수가 다를수가 있다.
- VoxSegNet
- Synchronized Spectral CNN (SyncSpecCNN)
- Shape Fully Convolutional Networks (SFCN)
- CoSegNet
- Branched AutoEncoder network (BAE-NET)
- top-down recursive part decomposition network (PartNet)
- zero shot 3D part segmentation
5.4 3D POINT CLOUD SEGMENTATION Summary
- regular data representation덕분에 projection-based methods 과 discretization-based methods 둘 다 2D Image를 network architecture 에 활용할 수 있게 되었다.
- 하지만, 3D-2D projection에 의해서 야기되는 projection-based methods 의 한계때문에 information loss를 수반하게 되고, discretization-based methods은 해상도의 증가로 인한 계산량이 3제곱으로 증가한다는 것이다.
- 이를 극복하기 위해 indexing structures를 기반으로 하는 sparse convolution이 실현 가능한 해결책이 될 수 있으며 추가로 연구할 가치가 있다.
- Point-based networks은 가장 많이 연구되는 방법이다.
- 하지만, point representation은 기본적으로 명시적으로 주변 Point들의 정보를 가지고 있지 않기 때문에, 현재 나와있는 대부분의 Point-Base 방법은 비용이 많이 드는 neighbor searching mechanisms에 의존하고 있다.
- 이런 점은 기본적으로 Point-based 방법들의 효율을 제한하고 있다. 최근 제안된 point-voxel joint representation은 이런 제안을 개선할 수 있는 흥미로운 연구이다.
- point cloud segmentation에 있어서 imbalanced data로 학습하는 것은 여전히 어려운 일이다.
- 비록 몇개의 접근 방식이 우수한 성능을 보여주기는 했지만, minority class에 대해서는 여전히 성능은 제한적이다.
- 현재 대부분의 방법들은 small point clouds (e.g.,1m×1m with 4096 points)에 대해서는 잘 동작한다.
- 실제로 depth sensor로 부터 받은 point cloud data는 대부분 대용량의 Data인 경우가 많다.
- 그래서 large-scale point clouds의 효과적인 segmentation에 대해서는 좀 더 연구하는 것이 바람직하다
- dynamic point clouds에서 spatio-temporal information을 학습하기 위한 소수의 연구가 시작되었습니다.
- spatio-temporal information이 3D object recognition , segmentation , completion등과 같은 부수적인 작업의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있으리라 기대하고 있습니다.